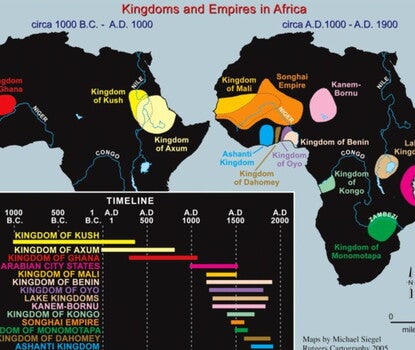
Kingdoms and Empires in Africa, ca. 1000 BC–AD 1900
by Michael Siegel, Rutgers Cartography
Visualize the geography and chronology of African kingdoms and empires through this map.
Photograph of Charles Remond Douglass
ca. 1864
Frederick Douglass’s youngest son served in the 54th Massachusetts Infantry.
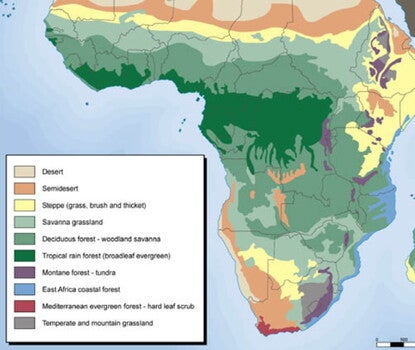
Vegetation of Africa
by Exploring Africa, Michigan State University
Visualize the varied vegetation zones of the African continent.
Ambrotype of African American Woman with Flag
1860s
This ambrotype features a woman believed to be a washerwoman for Union troops near Richmond, Virginia.
Painting of a Plantation
ca. 1860
Explore an artist’s depiction of enslavement.
Black Student Union Strike for Black Studies at San Francisco State College
1968
See the student protests that led to the first Black Studies department and gave rise to the field of African American studies.
“Walker’s Appeal”
1829
Black abolitionist David Walker wrote a powerful pamphlet on the effects of enslavement on African Americans and what enslaved people should do to escape.
Sugar Cane Harvest, Antigua, West Indies
1823
View this depiction of enslavement in the Caribbean.
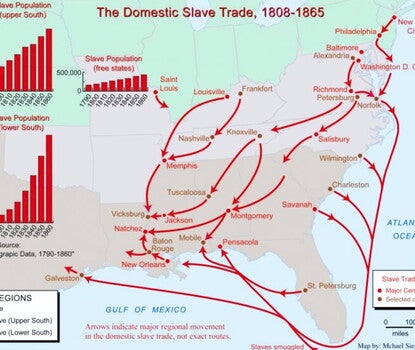
The Domestic Slave Trade, 1808–1865
by Michael Siegel and Rutgers Cartography
Explore data and geographical trends of the domestic slave trade in the nineteenth century.
Juan Garrido’s Probanza
1538
Read the narrative of a Congolese man’s experience in Mexico with the Spanish conquistadors.
Juan Garrido on a Spanish Expedition
1579
View this image that is believed to be Garrido alongside Hernán Cortés.
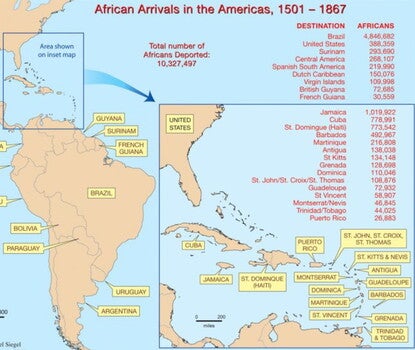
African Arrivals in the Americas, 1501–1867
by Michael Siegel and Rutgers Cartography
Visualize the impact of the displacement of Africans resulting from the transatlantic slave trade.
Showing results 61 - 72